The knee joint is subject to injury often in high-level athletes but also intermediate and low level ones as well. Lesions also can occur in elderly patients due to degenerative processes and violent contractions at a sharp bend of the knee, endangering the knee extensor apparatus by disruption of its elements at either the quadriceps tendon at its insertion into the pole top of the patella or the patellar tendon at its patellar insertion, or insertion into the anterior tibial tuberosity or body of the tendon.
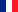
The Figure. 37 shows what is known as the extensor of the knee.

Figure. 37 shows the extender device in front, consisting of a large group of muscles, bones, and two main tendons.
What is known as non-traumatic problems or micro trauma also known as Osgood syndrome (constant and repeated tension during growth generating an avulsion of cartilage as well as tendon pain.) Sinding Larsen (resembles the above but pertains to the tip of the patella) Figure 37 shows both cases.

Figure. 38. To the left, Osgood syndrome. To the right Sinding Larsen.
What you need to know is that it is seen more frequently in adolescents, the pain increases with exercise, affects both knees, and certain movements increase the pain.
There should be a temporary pause in the practice of a sport, if there is much pain we can provide a temporary immobilization to rest the joint for a small amount of time, not to be infiltrated with products such as steroids, long evolution up to 18 months, usually improves without surgery and it may be necessary to remove that bone mass or "comb the tendon", do not worry it is not painful.
As for Traumatic Problems
The muscle breakdown (where a concussion, a laceration or tear fibers may take place; is seen in brutal exercises stretches, with rest and immobilization fibers may heal, in cases where there is total muscle rupture surgical treatment is necessary) Figure . 39 and 40

Figure 39 rupture, without pre-stretching exercise. See arrow.

Figure 40. Total rupture of the muscle. See arrow. Surgical indication.
Ruptures of the quadriceps tendon and patellar tendon
The rupture usually occurs in people who have previously suffered tendinitis where the tendon has deteriorated or patients who have suffered trauma in the tendon. There are also many diseases that weaken the tendon and may favor rupture as are rheumatic diseases, renal failure, and medications such as steroids or antibiotics such as quinolones, but it may also be a spontaneous rupture).
Clinically, there is a lot of pain and inability to lift the leg and the kneecap is mainly above or below where it should be (Figure 41 and 42).

Figure. 41. Quadriceps tendon rupture, the patella slides downwards

Figure. 42. Patellar tendon rupture, in comparison to the quadriceps, the patella slides upwards
Treatment
Is Surgical and the modality depends on the school, in France early treatment is recommended, some people temporarily unable to adapt to this situation and come after a long time, in such cases one speaks of a chronic rupture where treatment is a little heavier with a full system transplant extender.
Which can take a graft organ bank or part of your other knee each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Finally in cases where fracture of the patella or tibial tuberosity, reduction and internal fixation is the best indicación.vease Figure 43.

Figure 43. Fractured left kneecap and right reduction and fixation.
The other type of disruption of the extensor apparatus is the tibial tuberosity avulsion, where the patellar tendon insertion. Figure 44 shows the avulsed left and right correction.

Figure 44. Avulsion of the tuberosity and screw repair.
Stiffness in the hip and knee
The front thigh muscles tension can be caused by problems such as poor posture, stiffness in the joints of the hip, the rigid spine or too much neural stimulation in the thigh and hip flexors. The rigidity of the hip can do that you can move the joints of the same in all ranges of motion, rotation, flexion and extension. In knee extension Contracture is a well-known complication of severe femoral fractures, especially in the supracondilar region. What happens is the replacement of muscle tissue by fibrous tissue or accumulation of collagen fibers. The deformity is primarily secondary to contraction of the quadriceps and all the extensor mechanism suffers adhesions as mentioned above., knee extension stiffness can be intra-articular, associated with atrophy brosis or partial, affecting only the patellofemoral area. Participation of the inner collateral ligament that is at its maximum at 60 ° bending length is shortened with prolonged detentions causes extrarticulares has also been described are adhesions quadriceps by fibrosis to the femur in the fracture focus already the postsurgical scars, 3rd in the path of the fixing screws influence4., is also found in patients who remain large periods of time in knee extension who develop secondary contracture of the mechanism Extender in presenting quadriceps atrophy, is fibrous and shortens by restricting the knee flexion.
Initially according to the time and degree of rigidity, the release with Holmiun laser yag or laser 4th generation candles (both available in the unit) it is possible to get an extension and flexion are acceptable, but if the rigidity is important or old (several years) probably need to be associated with the laser technique a JUDET release.
Judet cuadriceplastia is a surgery that is performed by sequential steps and according to be achieved to improve the mobility will be continuing to the next step, stopping when you get adequate mobility. The incision starts at the knee and as structures released enlarges the scar in the direction of the hip, the aim is to get at least 90 degrees flexion, rehabilitation plays an important role in the recovery of muscle strength and maintenance of the amplitudes obtained joint intervention. This technique of Judet addresses sequentially components that block the extension of the knee and hip.
Figure 1: shows the set of structures forming the extensor apparatus, which must be released progressively.